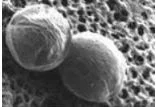
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a type of intestinal bacteria that cause the majority of ulcers in the stomach and duodenum. They thrive in highly acidic environments and have a unique way of adapting to the harsh environment of the stomach. H. pylori have been classified as low-potential carcinogens (cancer-causing substances) by the World Health Organization.