Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a type of intestinal bacteria that cause the majority of ulcers in the stomach and duodenum. They thrive in highly acidic environments and have a unique way of adapting to the harsh environment of the stomach. H. pylori have been classified as low-potential carcinogens (cancer-causing substances) by the World Health Organization.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis is the name for several different illnesses all caused by an inflammation of the liver. Drinking alcohol and taking drugs can cause hepatitis, but it can also be caused by a viral infection. Hepatitis A is a disease caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV). It is the most common type of hepatitis, with at least 1.4 million reported cases world wide every year.
Human Rights
Under international human rights laws, water is protected as a human right. In the 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the 1966 International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, and the 1966 International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, water is not explicitly mentioned as a human right. It was, however, implied through other human rights, such as the right to life, right to an adequate standard of living, and the right to health.
Industrial Waste
Industrial waste is defined as waste generated by manufacturing or industrial processes. The types of industrial waste generated include cafeteria garbage, dirt and gravel, masonry and concrete, scrap metals, trash, oil, solvents, chemicals, weed grass and trees, wood and scrap lumber, and similar wastes. Industrial solid waste - which may be solid, liquid or gases held in containers - is divided into hazardous and non-hazardous waste.
Inuktitut
Lead in Drinking Water
Lead is a toxic metal found in natural deposits. It can be found in air, soil, dust, food, and water. Lead was commonly used in household plumbing materials and water service lines until 1986. The National Plumbing Code allowed lead as an acceptable material for pipes until 1975 and in solder until 1986. All provinces and territories use the National Plumbing Code as a basis for their own regulations. Regulations regarding lead used in plumbing materials were phased in across the country. Therefore, the timing of when lead service lines and other lead-based plumbing materials stopped being used may differ depending on where you live.
Legionella
Liquid Candy and Its Health Effects
Marine Dumping
Marine Dumping has been defined as the deliberate disposal at sea of wastes or other matter from vessels, aircraft, platforms or other man-made structures, as well as the deliberate disposal of these vessels or platforms themselves. Marine dumping can destroy or degrade important habitats for aquatic species and cause coastal erosion and salutation, which affect the health and productivity of the marine environment.
Microplastics
Plastics are all around us, from the clothes we wear and the packaging that contains our food to construction materials in our homes and much more. Microplastics are small pieces of plastic that are less than 5 millimetres long. Microplastics can come from a variety of sources. They can come from plastic that has broken apart or resin pellets used for plastic manufacturing or in the form of microbeads. They can also be found in the fabric of synthetic clothing.
Mining and Water Pollution
While there have been improvements to mining practices in recent years, significant environmental risks remain. Negative impacts can vary from the sedimentation caused by poorly built roads during exploration through to the sediment, and disturbance of water during mine construction. Water pollution from mine waste rock and tailings may need to be managed for decades, if not centuries, after closure.
Oil Fields
Many mining operators believe that technology will be able to find a solution to the extreme environmental damage that mining operations cause. This is a case of counting the chickens before they hatch, because hazardous wastes are piling up and large areas of land are being left bare, with few plants, trees and wildlife, as mining companies move to more oil-rich areas. Mining companies are quick to point out that recent efficiencies mean that less water and natural gas are required to produce each barrel of oil; industry official say that water is reused up to 17 times. Efficiencies are good, but the increase in oil production requires more water and natural gas than ever before, meaning that these resources are not being conserved.
Oil Spills
Ojibway
According to the 2001 Canadian census, there are approximately 21,000 people across Canada who speak the Ojibway language. Nearly all of these live in Ontario (9,670 people) and Manitoba (8,840 people). Nationally, the Ojibway language is the third most spoken language; Cree and Inuktitut are spoken by more people.
Pathogenic Microbes
Some people believe that all that is required to produce safe water is to have a chlorine residual in the water. This, unfortunately, is not correct. The presence of particles will, in fact, shield pathogenic microbes from being killed by chlorine or other disinfectants. It is, therefore, important to remember that only good quality water can be safely disinfected.
Persistent Organic Pollutants
POPs are a group of man-made substances, most of which share characteristics like low water solubility (they do not easily dissolve in water), the ability to accumulate in fat (high lipophilicity), and resistance to biodegradation (they take a very long time to break down and stop being harmful). The name POPs refers to many pollutants such as pesticides like DDT and pollutants like PCBs. These chemicals come from pesticides, industrial chemicals, and are the unwanted by-products of industrial processes or combustion.
Pesticides and Water Pollution
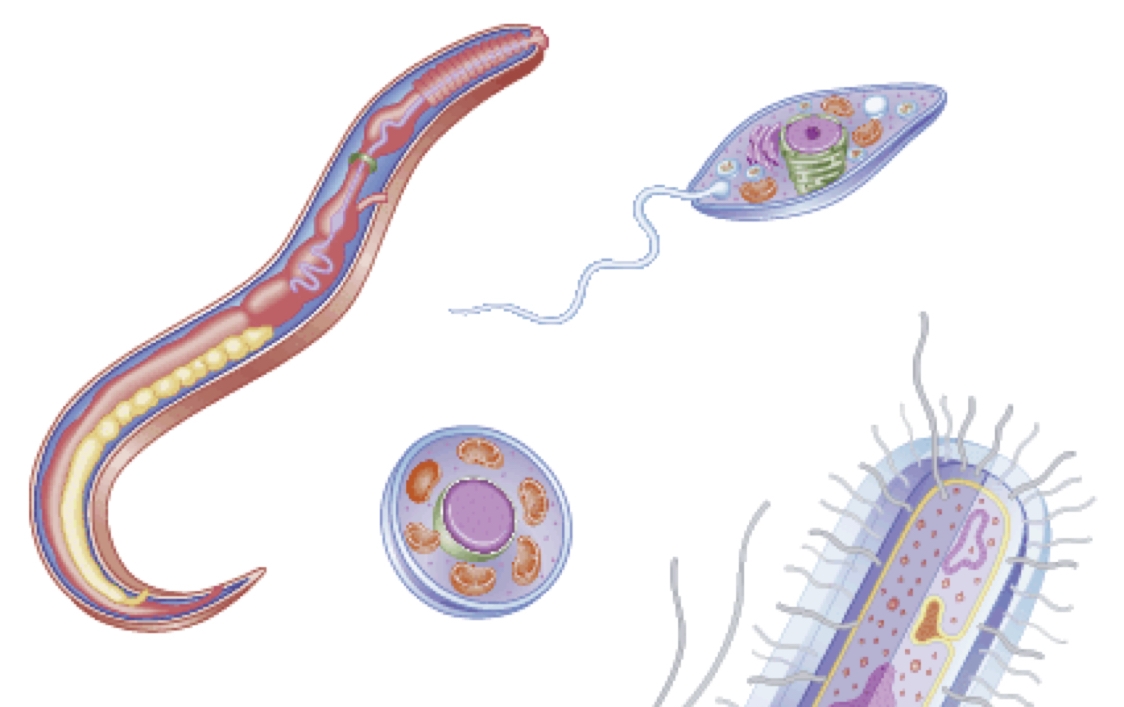
Protozoan Parasites
A protozoan is what we call a eukaryotic organism because it is a cell that contains a true nucleus and is bounded by a nuclear membrane. It consists of only a single cell and is so small that we usually can’t see it without using a microscope. The protozoa group is very diverse and has about 50 000 members, each with its own personal characteristics - almost like how every human being is different from another.
Shigella
Solar Water Distillation
Solar water distillation is the process of using energy from the sunlight to separate freshwater from salts or other contaminants. The untreated water absorbs heat, slowly reaching high temperatures. The heat causes the water to evaporate, cool, and condense into vapour, leaving the contaminants behind.